Media
What the sea spider genome reveals about their bizarre anatomy
The first high-quality pycnogonid genome provides novel insights in chelicerate evo-devo
The first high-quality pycnogonid genome provides novel insights in chelicerate evo-devo
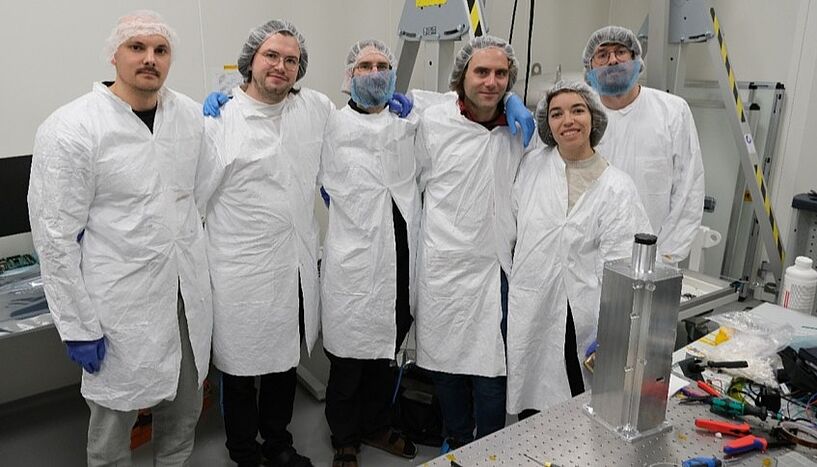

Communication with the satellite will be established in the next two weeks
26.06.2025 | [weiter]

Eight young researchers from the University of Vienna impressed the FWF Board of Directors with their excellent research projects
24.06.2025 | [weiter]

Even short-term high fructose consumption increases the concentration of receptors to which bacterial toxins can bind
24.06.2025 | [weiter]

Research about language, literature, history and culture of Ukraine
18.06.2025 | [weiter]
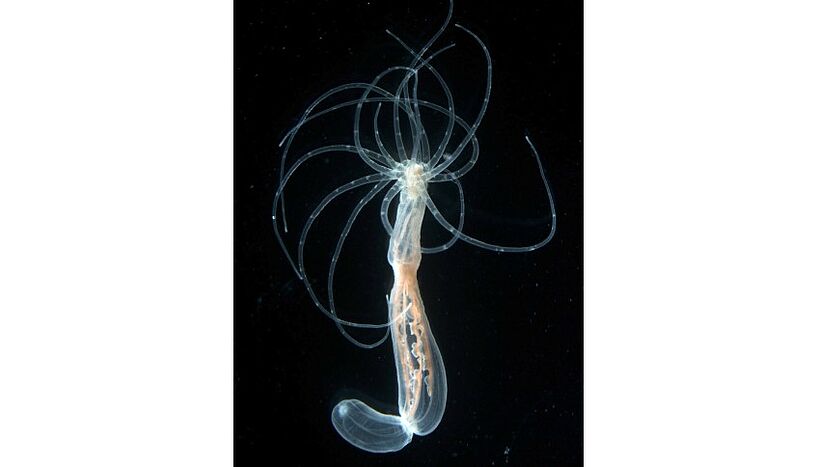

New insights into the evolution of the back-belly-axis
13.06.2025 | [weiter]
New findings published in Nature Photonics
06.06.2025 | [weiter]
New insights show universal applicability of carbyne as a sensor
26.05.2025 | [weiter]

Term of office from 1 October 2026 until 30 September 2030
19.05.2025 | [weiter]