Parrots’ go to carpentry school
03. September 2014The social transmission of innovations between cockatoos
Scientists from Oxford University, the University of Vienna, and the Max Planck Institute at Seewiesen have shown that a spontaneous innovation by a Goffin’s cockatoo can spread to other conspecifics by social learning.
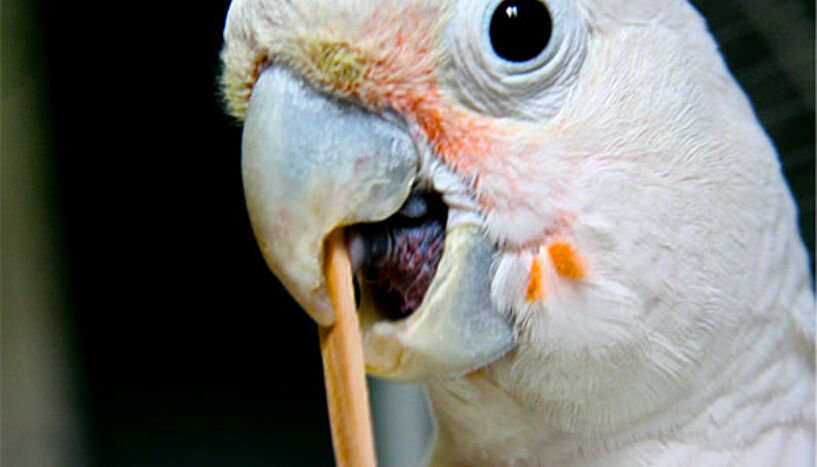
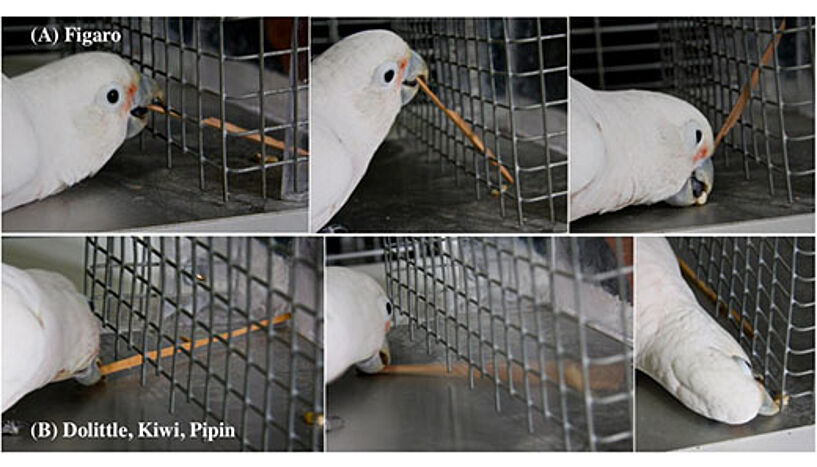
After observing that an adult male Goffin cockatoo named Figaro spontaneously started to sculpt stick tools out of wooden aviary beams to use them for raking in nuts out of his reach, the researchers wondered what effect, if any, such individual invention might have on social companions. They used Figaro as a role model and treated other birds to different degrees of exposure of his crafts.
One experimental cockatoo group were allowed to observe Figaro skilfully employing a ready-made stick tool, while another could see what researchers call "ghost demonstrations", either seeing the tools displacing the nuts by themselves, while being controlled by magnets hidden under a table, or seeing the nuts moving towards Figaro without his intervention, again using magnets to displace the food. They were all then placed in front of the same problem, with a ready-made tool lying on the ground nearby.
Three males and three females that saw Figaro’s complete demonstration interacted much more with potential tools and other components of the problem than those seeing ghost demos. Remarkably, all three males in this group acquired proficient tool use, while neither the females in the same group, nor males and females in the ghost demonstration groups did. "This is the first experimentally controlled evidence for the social transmission of an original tool use event in any non-habitually tool using bird so far", says Stefan Weber, a student from the University of Vienna, who was involved in the data collection.
The successful birds did not just imitate Figaro’s movements: their tool-use techniques were themselves new. While Figaro held tools by their tips, inserted them through the cage grid at different heights and raked the nuts towards him while adjusting the tool’s position as the target moved closer, the successful observers laid the sticks on the ground and propelled the nuts into their reach by a quick ballistic flipping movement.
The latter technique was arguably more efficient for the test circumstances, which differed from those in which Figaro had made his first discovery; the pupils in this sense surpassed the teacher’s performance. "Although watching Figaro was necessary for their success they did not imitate his exact motor activities. Successful observers seemed to attend to the result of Figaro’s interaction with the tool but developed their own strategies for reaching the same result, rather than copying his actions. This is typical of what psychologists would call emulation learning", explains Dr. Alice Auersperg who led the study at the Goffin Lab at the University of Vienna.
Two of the successful observers were later tested in the absence of ready-made tools, but offering them suitable tool-making material. One of them spontaneously started to make his own tools out of a wooden block, while the other initially failed, but then did so after a single demonstration session watching Figaro carve tools out of a block. "While inconclusive, this indicates that learning to use tools may per se stimulate the acquisition of tool-making, which is more distant from the target behaviour", adds Dr. Auersperg.
Prof. Alex Kacelnik from the University of Oxford is particularly interested in the differences between the behaviour of demonstrator and observers: "There is a substantial difference between repeating a teacher’s behaviour and emulating his or her achievements while creating one’s own methods. The latter implies a creative process stimulated by a social interaction, while the former could, at least potentially, rely on simpler imitation. The cockatoos seem to emulate and surpass their teacher, which is what all good professors hope for their best students".
Goffin-Lab
Movie 1, Tool use techniques of the demonstrator and the successful observers:
http://www.zoo.ox.ac.uk/group/kacelnik/goffin_cockatoos_social_transmission.mov
Movie 2, Tool manufacture example Figaro, Dolittle & Kiwi:
http://www.zoo.ox.ac.uk/group/kacelnik/goffin_cockatoos_tool_making.mov
Publication in "Proceedings of the Royal Society B":
Auersperg, AMI, von Bayern, AMP, Weber, S, Szabadvari, A, Bugnyar, T, Kacelnik, A. Social transmission of tool use and tool manufacture in Goffin cockatoos (Cacatua goffini) 2014. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 20140972.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2014.0972
Scientific Contact
Dr. Alice Auersperg
Department of Cognitive Biology
University of Vienna
1090 Vienna, Althanstraße 14
T +43-1-4277-761 01
M +43-676-939 03 92
alice.auersperg(at)univie.ac.at
Press Contact
Mag. Veronika Schallhart
Press OfficeUniversity of Vienna
1010 Vienna, Universitätsring 1
T +43-1-4277-175 30
M +43-664-602 77-175 30
veronika.schallhart(at)univie.ac.at
Wissenschaftlicher Kontakt
Dr. Alice Auersperg
Head of Goffin Lab – Messerli ForschungsinstitutVeterinärmedizinische Universität Wien
, 1210 - Wien, Veterinärplatz 1
+43-676-939 03 92
alice.auersperg@vetmeduni.ac.at
Rückfragehinweis
Mag. Veronika Schallhart
DLE ÖffentlichkeitsarbeitUniversität Wien
1010 - Wien, Universitätsring 1
+43-1-4277-17530
+43-664-8176793
veronika.schallhart@univie.ac.at
Downloads:
Figaro_Tool_c_Auersperg_02.png
Dateigröße: 2,01 MB
STT_Figure_3_c_Auersperg_01.jpg
Dateigröße: 1,02 MB
STT_ESM_Figure_c_Auersperg_en_01.jpg
Dateigröße: 396,21 KB